The Silent Threat in Your Home
A carbon monoxide leak can turn your safe haven into a deadly trap. This colorless, odorless gas is responsible for hundreds of deaths and over 100,000 emergency room visits in the U.S. annually.
Key Carbon Monoxide Leak Risks:
- Common sources: Gas furnaces, water heaters, fireplaces, and attached garages
- Warning signs: Yellow pilot lights, soot stains, and window condensation
- Health symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, and nausea that improve when you leave home
- High-risk groups: Children, the elderly, pregnant women, and those with heart or lung conditions
- Prevention: Install CO detectors and schedule annual appliance inspections
Carbon monoxide (CO) forms when fuel doesn’t burn completely in appliances like your furnace or water heater. When you breathe it in, CO molecules replace oxygen in your red blood cells, suffocating your body at a cellular level. Your brain and heart suffer first.
In Southern California, aging HVAC systems and poor ventilation can create the perfect conditions for a CO buildup. Many homeowners don’t realize their appliances could be silently poisoning their families.
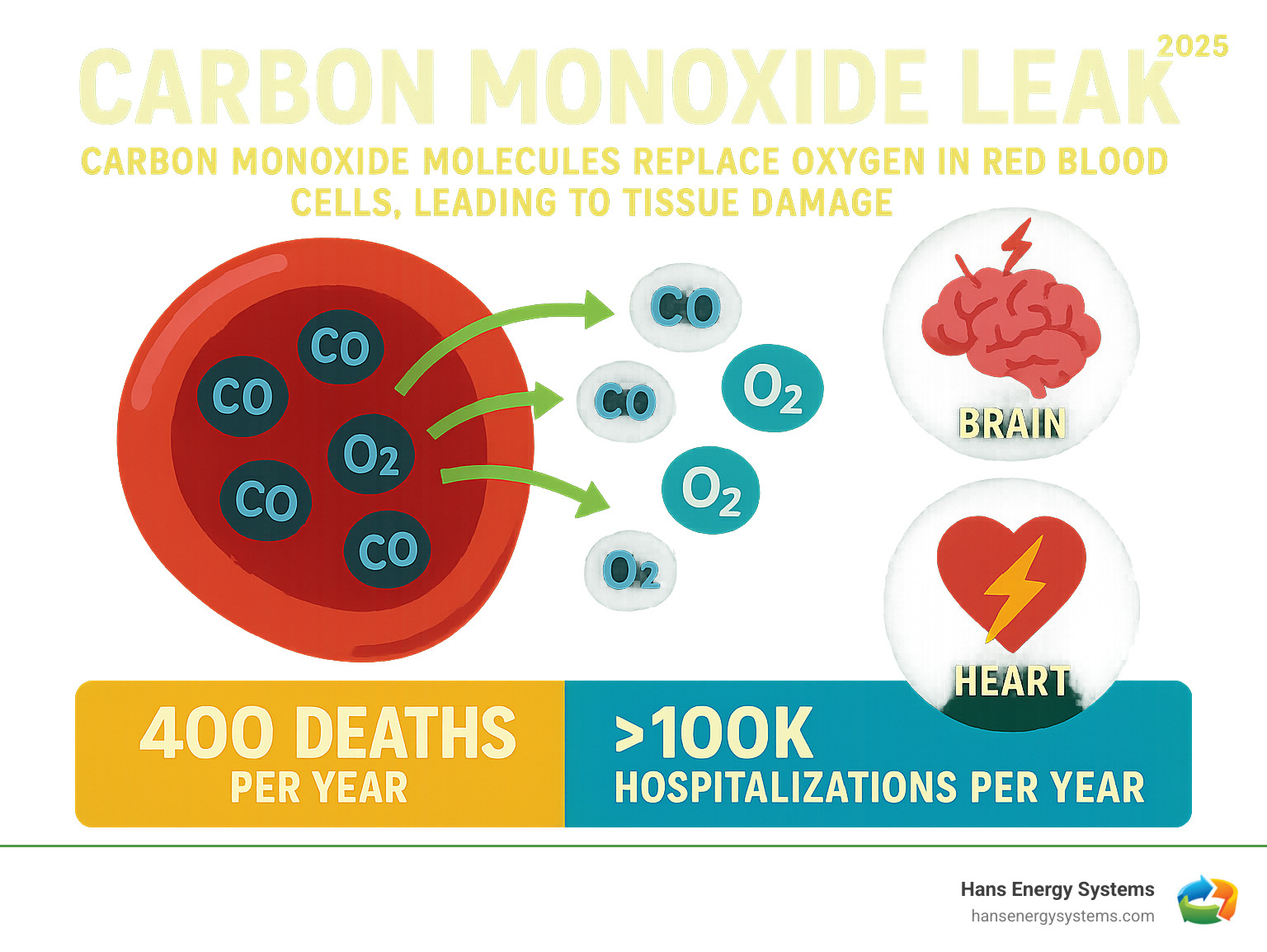
What is Carbon Monoxide and Why is it Dangerous?
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an invisible, odorless, and tasteless gas, earning it the nickname “the invisible killer.” This poisonous gas can cause serious harm or death within minutes.
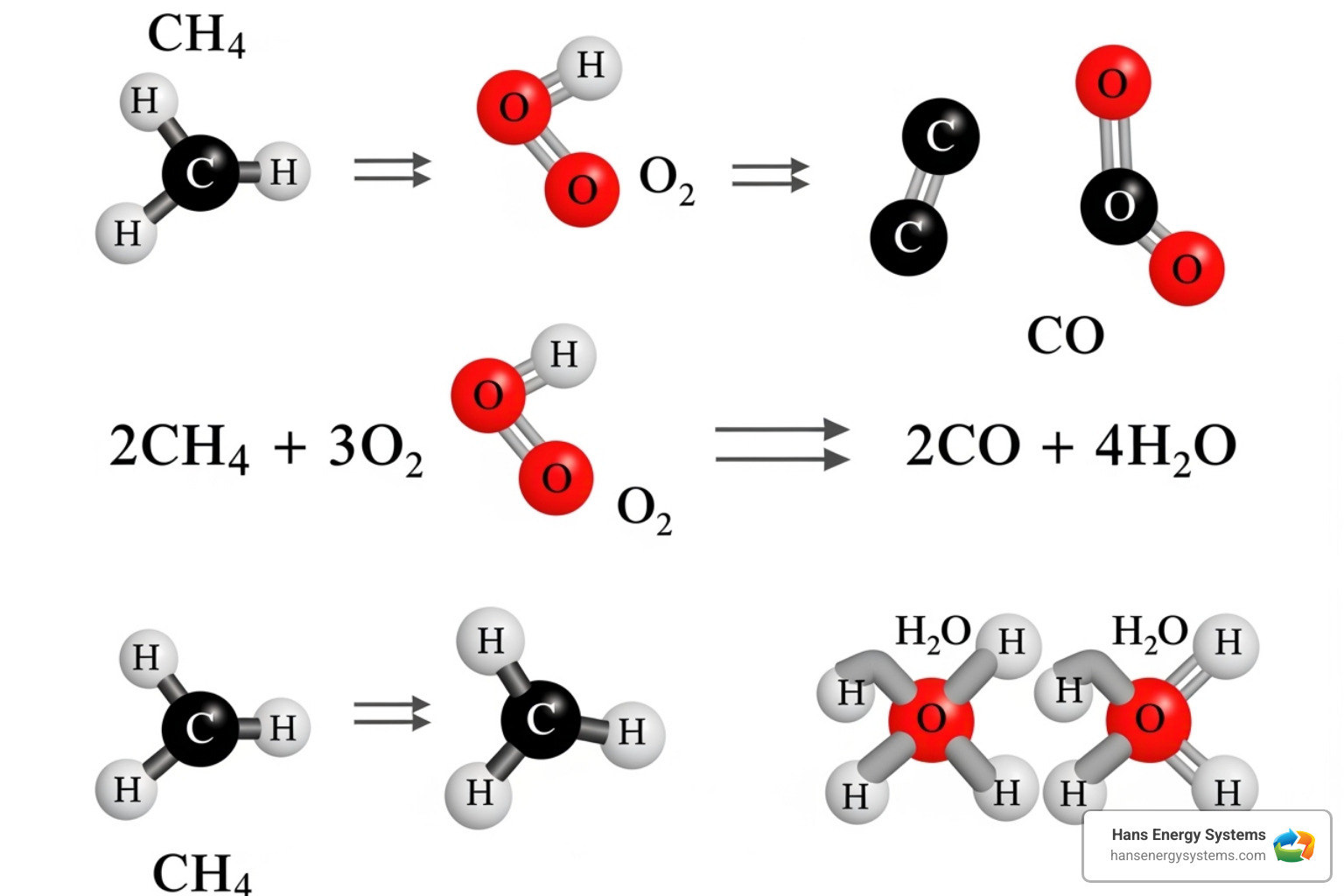
CO is produced by incomplete combustion when common household fuels don’t burn completely. Appliances like gas furnaces, water heaters, fireplaces, and even car engines can produce CO if they lack sufficient oxygen or have ventilation issues.
When you breathe in carbon monoxide, it enters your bloodstream and binds to your red blood cells about 200 times more effectively than oxygen. This leads to severe oxygen deprivation, as your cells are starved of the oxygen they need to function. Early flu-like symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and nausea are common, which is why CO poisoning is often dismissed as a minor illness. A key indicator is feeling worse at home and better when you leave.
For more details, you can watch this video: What is carbon monoxide? or visit the CDC’s page on Carbon Monoxide (CO) Poisoning Basics.
How Carbon Monoxide Affects the Body
CO causes suffocation at a cellular level, leading to tissue damage. Your brain and heart are the most vulnerable because they require the most oxygen. Even brief exposure can cause permanent brain damage, affecting memory and cognitive function. The strain on your heart can also lead to lasting heart damage.
Key Statistics on CO Poisoning
The statistics highlight the danger:
- Annual fatalities: The CDC estimates around 400 unintentional deaths from CO poisoning each year in the U.S.
- Emergency room visits: Over 100,000 people visit the ER annually for CO exposure.
- Hospitalizations: More than 14,000 people are hospitalized each year.
Most of these incidents are preventable with proper appliance maintenance and CO detection.
Common Sources of a Carbon Monoxide Leak in Your Home
Carbon monoxide leaks are almost always caused by fuel-burning equipment that is malfunctioning, poorly maintained, or used incorrectly. Any appliance that burns fuel can be a potential source.
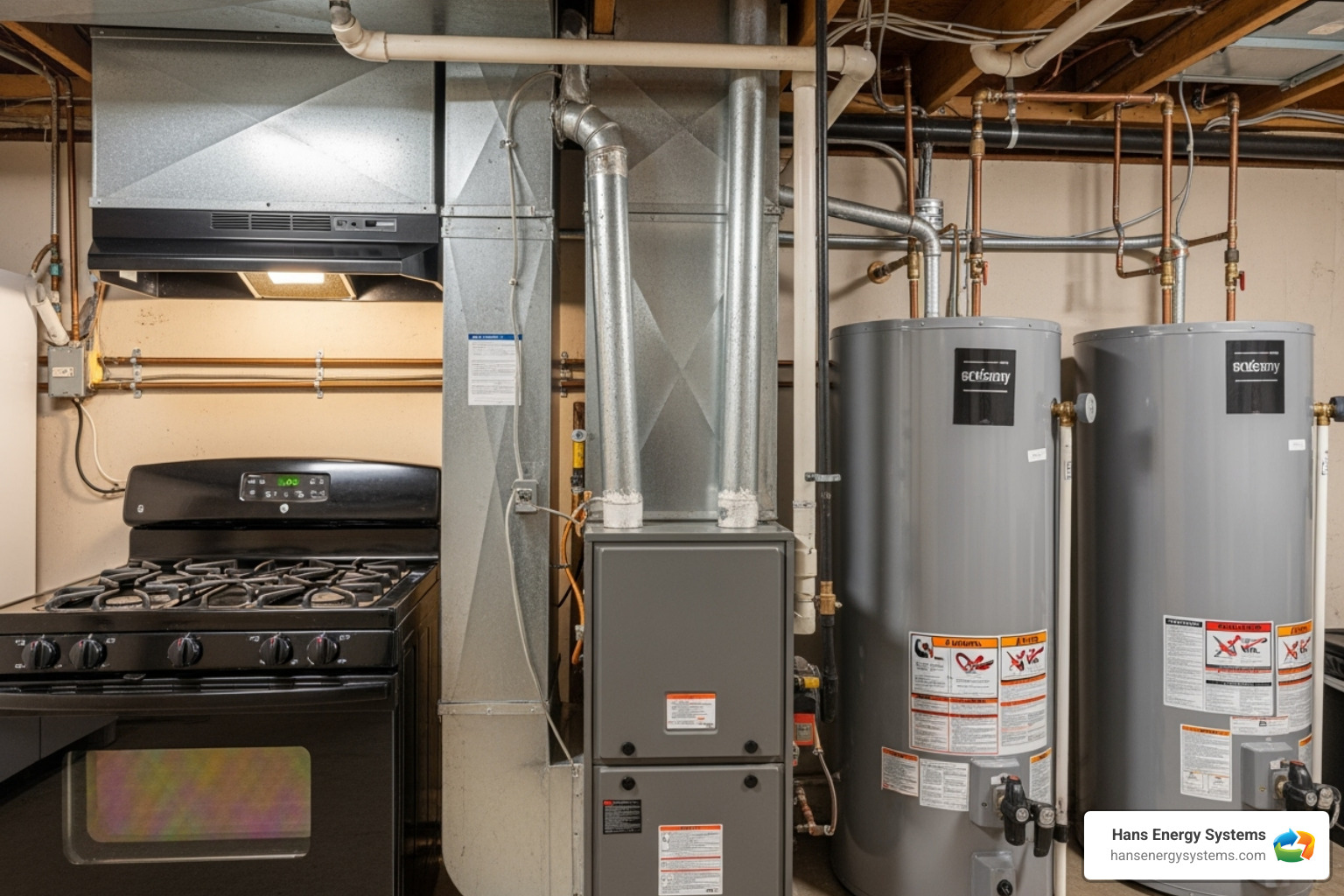

If you notice issues with your heating system, our guide on Signs You Need Heating Repair in Poway can help you identify potential problems.
Faulty HVAC Systems and Appliances
Your HVAC system is a common source of CO leaks. Problems often develop gradually and can include:
- Poor installation or maintenance: Incorrect installation or a lack of maintenance can lead to dangerous conditions. A cracked heat exchanger in a furnace can mix CO directly with your home’s air.
- Blocked vents: Vents for furnaces, water heaters, and gas clothes dryers can become clogged with debris, forcing CO back into your home.
- Malfunctioning Appliances: Gas stoves with improperly adjusted burners or fireplaces with blocked chimneys can also produce CO.
Regular professional maintenance is crucial for catching these issues early. Our article on Heating Problems and Solutions in Poway provides more detail on common heating issues.
Other Household and Garage Sources
Beyond major appliances, other common sources can create a dangerous carbon monoxide leak:
- Attached garages: Never run a car in an attached garage, even for a moment. Vehicle exhaust can quickly seep into your living space.
- Portable fuel-burning devices: Portable generators, charcoal grills, and camping stoves produce large amounts of CO and must only be used outdoors, far away from windows and doors.
- Wood stoves and fireplaces: Blocked chimneys can cause CO to back up into your home. Regular cleaning is essential.
- Gas-powered tools: Small engines on tools like lawnmowers and pressure washers also produce CO and should not be used in enclosed spaces.
Recognizing the Signs: Leaks and Poisoning Symptoms
Since carbon monoxide is undetectable by human senses, you must learn to spot the subtle clues of a carbon monoxide leak from your appliances and your own body.
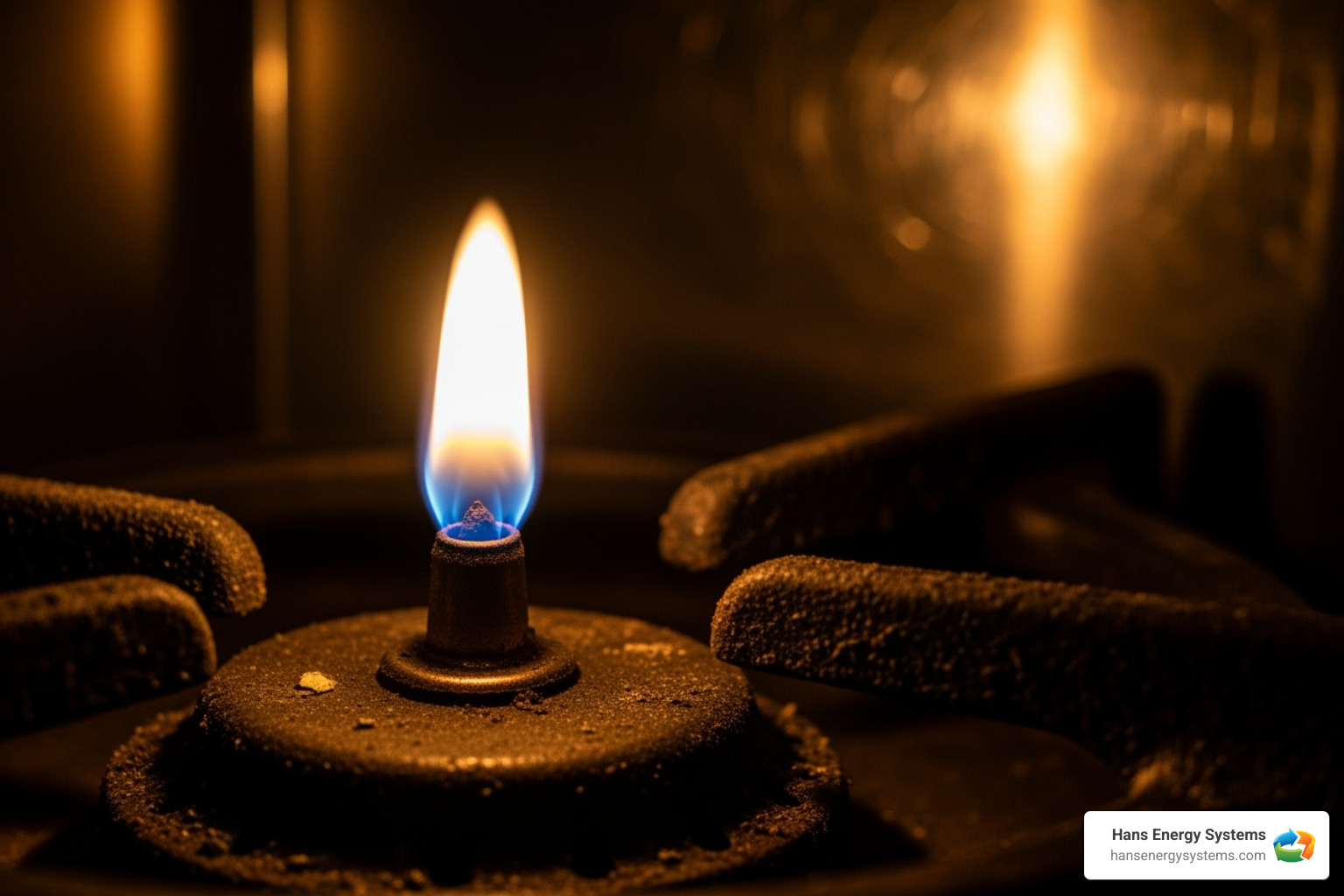

Physical Signs of a Carbon Monoxide Leak
Look for these warning signs around your fuel-burning appliances:
- Sooty or yellow-brown stains near the appliance.
- Fallen soot from a chimney or fireplace.
- A lazy, flickering yellow burner flame instead of a crisp blue one.
- Heavy condensation on windows near the appliance.
- Stale, stuffy air or unusual smells.
- Pilot light issues, such as the light frequently going out.
Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
CO poisoning symptoms mimic common illnesses like the flu, but there are key differences. Initial symptoms include headaches, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and shortness of breath. As exposure continues, it can lead to confusion, blurred vision, chest pain, and loss of consciousness.
The most important clue is that symptoms improve when you leave the house and worsen when you return. If multiple people (or pets) in the home experience these symptoms simultaneously, suspect a carbon monoxide leak immediately.
| Symptom | Carbon Monoxide Poisoning | Common Flu |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | Yes, often persistent | Yes |
| Dizziness/Weakness | Yes | Yes |
| Nausea/Vomiting | Yes | Yes |
| Shortness of Breath | Yes | Sometimes |
| Confusion | Yes | Less common |
| Blurred Vision | Yes | No |
| Chest Pain | Yes | No |
| Fever | No | Yes, typically high |
| Body Aches | Yes, generalized | Yes, often severe |
| Sore Throat/Cough | Less common | Yes |
| Improvement Outdoors | Yes | No |
| Multiple People Affected | Yes, often | Possible, but less common |
Trust your instincts. If you suspect a leak, take immediate action.
Prevention and Emergency Response
When dealing with a carbon monoxide leak, prevention is the best defense. Since you can’t detect this gas yourself, having the right safety measures and an emergency plan is life-saving.

Key prevention steps include annual inspections of fuel-burning appliances and ensuring proper ventilation. Our HVAC Services in Poway, CA include inspections to catch potential CO issues. It’s also vital to have an emergency plan so everyone in your family knows to evacuate immediately if a CO alarm sounds.
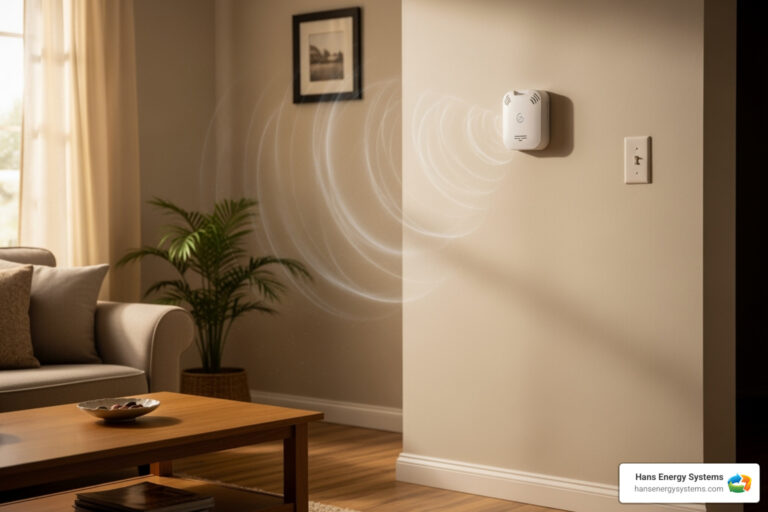
The Critical Role of Carbon Monoxide Detectors
CO detectors are your only reliable early warning system. Follow these best practices:
- Installation locations: Install detectors on every level of your home, especially near sleeping areas (within 10 feet of bedroom doors).
- Testing and Maintenance: Test alarms monthly and replace batteries annually (unless it’s a 10-year sealed unit).
- Alarm Lifespan: Replace the entire detector every 5-10 years, according to the manufacturer’s date on the unit. Their sensors wear out over time.
- Digital Readouts: Consider models with a digital display to see CO levels in parts per million (ppm).
This video demonstrates various Smoke and carbon monoxide alarms sounds. Detectors are a backup to, not a replacement for, regular professional maintenance.
What to Do If You Suspect a Carbon Monoxide Leak
If your CO alarm sounds or you suspect a leak, act immediately:
- Evacuate immediately: Get everyone, including pets, out of the house to fresh air. Do not stop to investigate or gather belongings.
- Call 911: Once safely outside, call 911 and report a suspected CO leak.
- Do not re-enter: Wait for emergency responders to test the air and declare it safe to go back inside.
- Seek medical attention: If anyone shows symptoms (headache, dizziness, nausea), inform medical personnel about the potential CO poisoning.
- Repair the source: After the emergency, have a qualified technician find and fix the source of the leak before using the appliance again.
Treat every CO alarm as a real emergency. A swift response can save lives.
Health Complications and At-Risk Individuals
A carbon monoxide leak can have lasting health consequences, even after a brief exposure. Some individuals are also at a much higher risk of severe poisoning.

The Mayo Clinic offers detailed information on the effects of Carbon monoxide poisoning – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic.
Long-Term Health Effects of CO Exposure
When CO deprives the brain and heart of oxygen, it can cause lasting damage. Survivors of serious poisoning may experience:
- Permanent brain damage: This can manifest as memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and personality changes.
- Neurological symptoms: Chronic headaches and movement disorders similar to Parkinson’s disease can develop, sometimes weeks after exposure.
- Heart conditions: The strain on the heart can lead to irregular heartbeats and reduced cardiac function.
- Chronic fatigue: Persistent weakness and exhaustion can significantly impact quality of life.
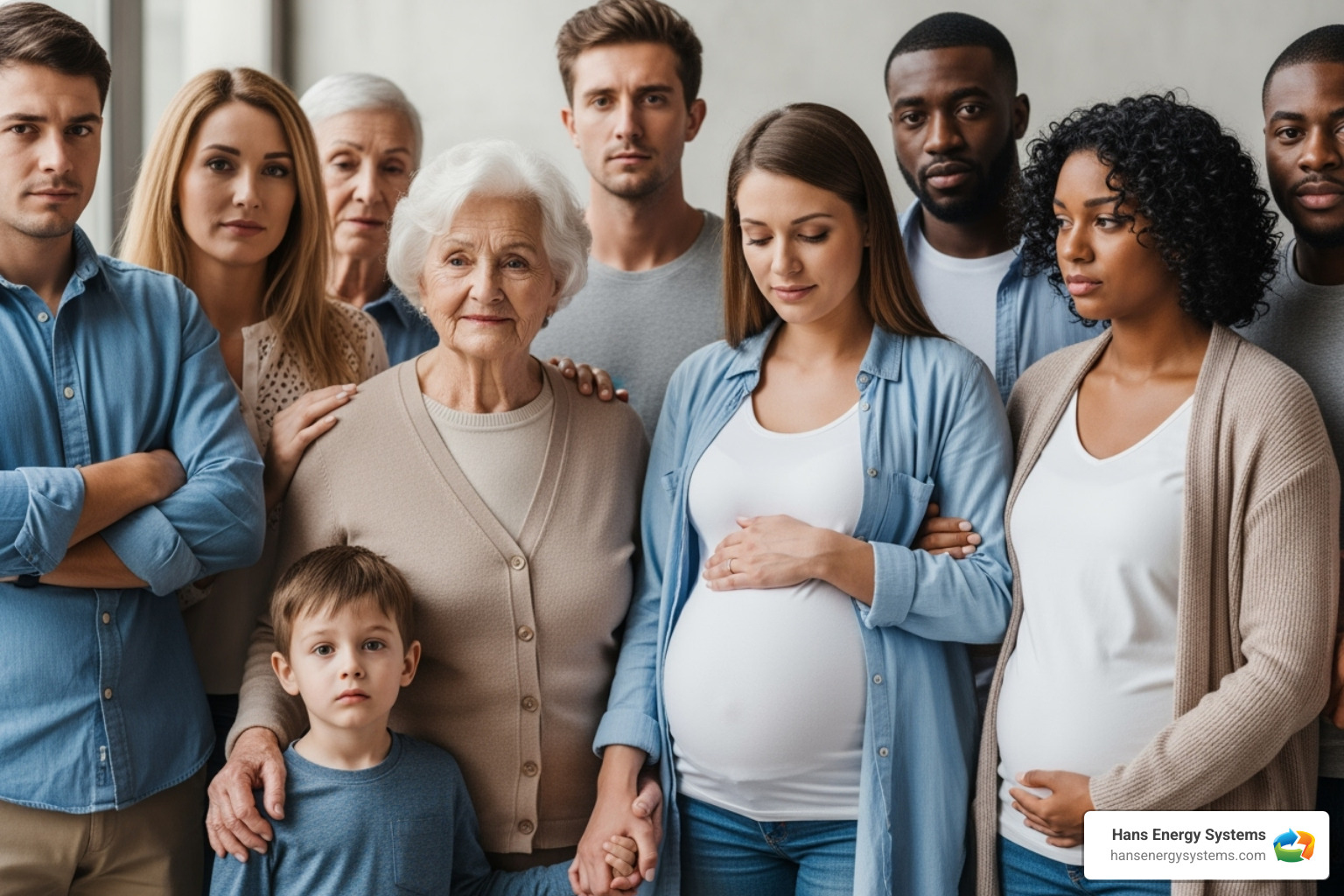
Who is Most at Risk?
While CO is dangerous for everyone, these groups are especially vulnerable:
- Infants and children: They breathe faster than adults and their developing brains are more susceptible to damage.
- Pregnant women: Fetal blood cells absorb CO more readily, posing a severe risk to the unborn baby.
- The elderly: Pre-existing conditions and a reduced ability to notice symptoms increase their risk.
- People with chronic health conditions: Those with chronic heart disease, anemia, or respiratory problems are more severely affected by oxygen deprivation.
- Sleeping or intoxicated individuals: They may not recognize symptoms before losing consciousness.
Frequently Asked Questions about Carbon Monoxide Safety
Here are answers to common questions about carbon monoxide safety.
Can a carbon monoxide leak cause a fire or explosion?
A carbon monoxide leak itself is not an explosion risk. However, the underlying problem causing the leak—such as a malfunctioning furnace or a natural gas leak—can be a significant fire or explosion hazard. This is why annual professional inspections of fuel-burning appliances are so important.
How long does it take to get carbon monoxide poisoning?
The time it takes depends on the concentration of CO in the air. At very high levels (1,600 parts per million or more), CO can be fatal within minutes. At lower levels, poisoning occurs gradually over hours, with symptoms that can be mistaken for the flu. Even long-term, low-level exposure can cause serious health issues, which is why CO detectors are essential.
Are electric appliances a source of carbon monoxide?
No. Electric appliances do not burn fuel, so they cannot produce carbon monoxide. The risk comes only from appliances that burn fuels like natural gas, propane, oil, wood, or gasoline.
Protect Your Home and Family from Carbon Monoxide
The threat of a carbon monoxide leak is serious, but preventable. This invisible gas, produced by the incomplete burning of fuel in common appliances like furnaces and water heaters, can be deadly. You can’t see, smell, or taste it, which is why proactive safety measures are essential.
Effective prevention includes:
- Installing CO detectors on every level of your home, especially near sleeping areas.
- Scheduling professional maintenance for all fuel-burning appliances annually. A qualified technician can identify and fix issues before they become dangerous.
- Using equipment safely: Keep portable generators and grills outdoors, and never run a car in an attached garage.
- Recognizing symptoms: If your family has flu-like symptoms that improve when you leave the house, evacuate immediately and call for help.
At Hans Energy Systems, we help protect families throughout San Diego County with reliable, professional HVAC maintenance. Regular inspections are about more than efficiency; they’re about safety and peace of mind. Our article on why Heating Repair Crucial for Poway Homes explains this further.
Don’t wait for an emergency. Take control of your family’s safety. Schedule your heating system inspection today with Hans Energy Systems.





